New Horizons Update: Spacecraft reveals Ultima Thule as entirely new world
The Kuiper Belt Object’s remarkable appearance illuminates the processes that built the planets four and a half billion years ago
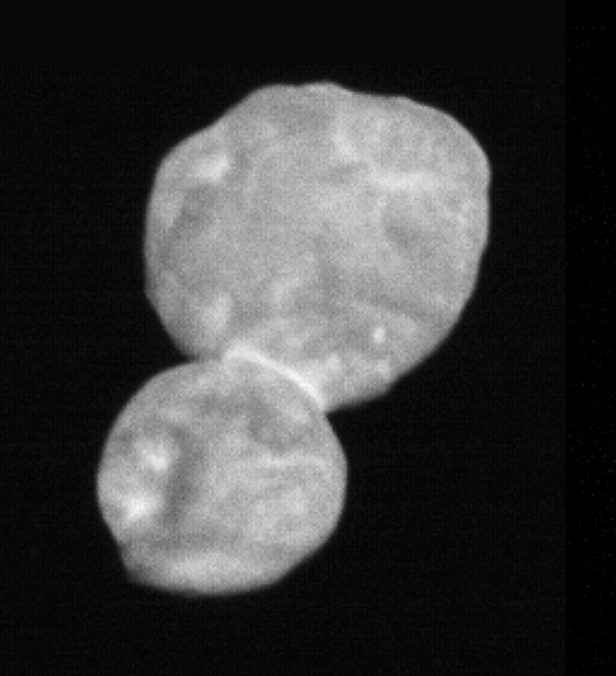
First image of Ultima Thule taken on 1 January 2019, just 30 minutes before closest approach from a range of 28,000 kilometres (18,000 miles). Image credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Southwest Research Institute
Scientists from NASA’s New Horizons mission released the first detailed images of the most distant object ever explored — the Kuiper Belt object nicknamed Ultima Thule. Its remarkable appearance illuminates the processes that built the planets four and a half billion years ago.
“This flyby is a historic achievement,” said New Horizons Principal Investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute in Boulder, Colorado. “Never before has any spacecraft team tracked down such a small body at such high speed so far away in the abyss of space. New Horizons has set a new bar for state-of-the-art spacecraft navigation.”
The new images — taken from as close as 27,000 kilometres (17,000 miles) on approach — revealed Ultima Thule as a “contact binary,” consisting of two connected spheres. End to end, the world measures 31 kilometres (19 miles) in length. The team has dubbed the larger sphere “Ultima” (19 kilometres/12 miles across) and the smaller sphere “Thule” (14 kilometres/ 9 miles across).
The team says that the two spheres likely joined as early as 99 per cent of the way back to the formation of the Solar System, colliding no faster than two cars in a fender-bender.
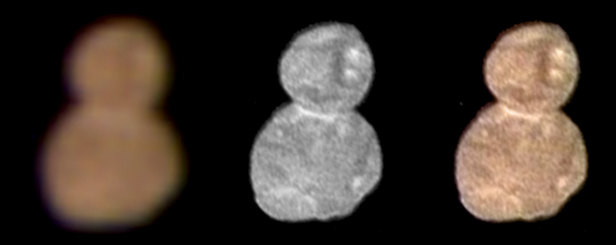
The first colour image of Ultima Thule highlights its reddish surface. At left is an enhanced-colour image taken by the Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC). Image credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Southwest Research Institute
“New Horizons is like a time machine, taking us back to the birth of the Solar System. We are seeing a physical representation of the beginning of planetary formation, frozen in time,” said Jeff Moore, New Horizons Geology and Geophysics team lead. “Studying Ultima Thule is helping us understand how planets form — both those in our own solar system and those orbiting other stars in our galaxy.”
Data from the New Year’s Day flyby will continue to arrive over the next weeks and months, with much higher resolution images yet to come.
“In the coming months, New Horizons will transmit dozens of data sets to Earth, and we’ll write new chapters in the story of Ultima Thule — and the Solar System,” said Helene Winters, New Horizons Project Manager.
The Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland, designed, built and operates the New Horizons spacecraft, and manages the mission for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate. The Southwest Research Institute, based in San Antonio, leads the science team, payload operations and encounter science planning. New Horizons is part of the New Frontiers Program managed by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama.
Keep up to date with the latest news in All About Space – available every month for just £4.99. Alternatively you can subscribe here for a fraction of the price!




